Do Wolverines Attack Humans? Wolverines, often regarded as one of the most fierce and intimidating creatures in the animal kingdom, have sparked fascination and fear alike.
These elusive, solitary creatures are known for their ferocious behavior, robust physical characteristics, and powerful instincts. However, despite their intimidating reputation, wolverine attacks on humans are rare, and the true nature of these interactions is often misunderstood.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into everything you need to know about wolverines, including whether or not they are likely to attack humans, the behaviors that may trigger such attacks, and most importantly, how to stay safe in their presence.
What Are Wolverines?
Wolverines, scientifically known as Gulo gulo, are members of the mustelid family, which includes animals such as otters, ferrets, martens, and badgers.
They are solitary, highly territorial animals that are widely regarded as fierce and relentless hunters.
Despite their relatively small size, they possess physical attributes that make them capable of surviving in harsh environments and fending off much larger predators.
Physical Characteristics of Wolverines
Wolverines are medium-sized carnivores, built with robust and muscular bodies that help them navigate through rugged terrains.
They weigh anywhere between 15 to 30 pounds and can measure up to 34 inches in body length, with an additional 10-12 inches for their bushy tails. Males are generally larger than females. Some key physical features include:
- Powerful Jaws: Wolverines have incredibly strong jaws capable of crushing bones. Their teeth and jaws are designed for tearing and consuming tough animal material, including the bones of their prey.
- Claws and Teeth: Their retractable claws are sharp, allowing them to climb and dig with ease. Their strong teeth and claws make them formidable predators and capable of defending themselves effectively when threatened.
- Fur Coat: Wolverines have a thick, dark fur coat, often adorned with lighter markings on their sides, which help insulate them against the harsh cold temperatures of their northern habitats. This thick fur is key to surviving in snowy and frigid conditions.
Behavior and Survival Instincts
Wolverines are solitary creatures by nature. Unlike many other predators that form packs, wolverines prefer to live and hunt alone, marking large territories to defend their resources and avoid competition.
These animals are also known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when it comes to protecting their territory or offspring.
As opportunistic feeders, wolverines are not averse to scavenging. They will often feast on carcasses left behind by larger predators such as wolves or bears.
In addition to scavenging, wolverines will hunt small prey like rodents, birds, and even larger prey such as deer or moose if the opportunity arises.
Their ability to cover vast distances is an important trait for their survival. Wolverines can roam over large territories, ranging from 200 to 500 square miles, searching for food. Their diet is highly varied and includes both scavenging and hunting.
Wolverine Habitat and Behavior
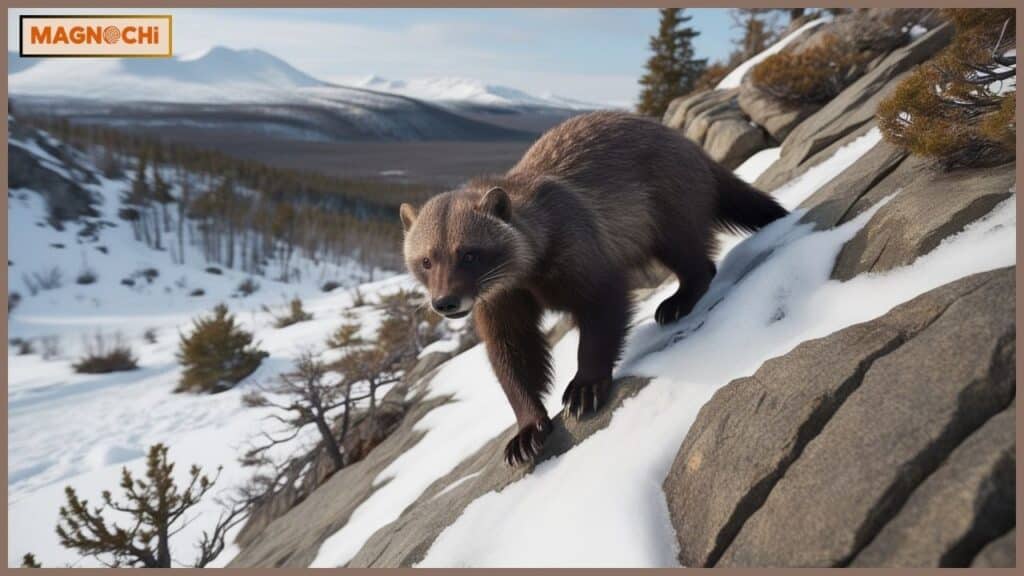

Natural Habitat of Wolverines
Wolverines are native to the Northern Hemisphere, primarily inhabiting the cold, rugged wilderness areas of Canada, Alaska, Scandinavia, and parts of Russia.
These regions offer the harsh environments that wolverines prefer, where the cold and remote landscape serves both as a hunting ground and a refuge from larger predators.
Wolverines are typically found in boreal forests, tundra, and mountainous terrains, all of which offer the snow cover, cold temperatures, and rugged terrain that wolverines need to thrive.
They are especially adapted to these cold environments, where they move through the snow with ease, seeking food in both forests and open landscapes.
Key Environmental Features:
- Boreal Forests: Stretching across the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia, boreal forests provide a dense habitat filled with coniferous trees, which offer shelter for wolverines during harsh winters.
- Tundra: Known for its permafrost and sparse vegetation, the tundra is home to various species, including wolverines, who rely on the open space to travel long distances in search of food.
- Mountainous Terrain: Wolverines are strong climbers and are often found in rocky or mountainous regions where they can hunt smaller animals or scavenge from larger predators.
Territorial Nature
Wolverines are highly territorial animals. They mark their territories with scent markings, often leaving behind droppings and urine to establish boundaries.
These territories can cover vast distances, with some wolverines traveling more than 30 miles in a day to patrol their space. Territorial disputes between wolverines can lead to violent encounters, especially when resources are scarce.
In addition to defending their territory from other wolverines, these animals will also guard their food sources, including the carcasses they scavenge from other predators.
While wolverines generally avoid human interaction, they will fight fiercely if they feel their territory is being encroached upon.
Do Wolverines Attack Humans?

General Behavior Towards Humans
Wolverines are elusive animals, meaning they generally avoid human interaction. They are solitary and shy creatures that tend to stay hidden in the wild.
Despite their aggressive behavior when defending themselves or their young, wolverines do not actively seek out humans as prey. In fact, most wolverines prefer to stay away from populated areas and human settlements, and they are rarely seen by humans.
However, there are instances where wolverines might attack or act aggressively, but these incidents are incredibly rare.
When wolverines do come into contact with humans, the encounter is typically due to the animal feeling threatened or provoked.
Circumstances Leading to Aggression
Wolverines are defensive by nature, and their aggression is usually a response to feeling threatened or cornered. The most common situations that could lead to a wolverine attack include:
- Protecting Their Offspring: A mother wolverine with young is extremely protective. If she feels her offspring are in danger, she will not hesitate to attack in defense.
- Defending Territory: Wolverines are fiercely territorial. If a human enters their space or gets too close to their den, the animal may see it as a threat and attack to protect its home.
- Feeling Cornered or Trapped: Like many animals, wolverines will fight if they feel trapped or cornered with no way of escaping. This type of aggressive behavior is a survival instinct, as wolverines rely on their strength and sharp claws to defend themselves from predators and other threats.
It’s essential to understand that these aggressive behaviors are rooted in survival and not predatory instincts. Unlike larger predators such as bears or wolves, wolverines are not typically interested in humans as prey.
Documented Wolverine Attacks
While wolverine attacks on humans are rare, they have been documented in specific cases where humans were in the vicinity of a wolverine’s territory.
Most attacks occur in remote, wilderness areas, where human presence is uncommon. Here are a few documented cases of wolverine encounters:
Case 1: Alaska (2010)
A trapper in Alaska was attacked by a wolverine while checking his traps. The wolverine, likely feeling threatened by the trapper’s presence, launched an aggressive defense of its territory.
The trapper was able to defend himself, but the attack left him with minor injuries from the wolverine’s claws and teeth. This case highlights that while attacks are rare, they can still happen when a wolverine feels its territory is being invaded.
Case 2: Canada (2015)
A hiker in Canada reported an encounter with a wolverine while trekking through a forested area. The hiker unknowingly entered the animal’s territory and was confronted by the wolverine, which showed signs of aggression.
The hiker was able to retreat without serious injury. This incident emphasizes the importance of understanding territorial behavior in wolverines and how staying on designated trails can help avoid these types of encounters.
Case 3: Scandinavia (2018)
In Scandinavia, a wildlife photographer unintentionally got too close to a wolverine den while trying to capture images. The wolverine, likely defending its den, charged at the photographer, but the individual managed to escape unharmed by backing away slowly.
The photographer later reported the encounter to local wildlife authorities, which helped raise awareness about the presence of wolverines in the area.
These real-life case studies demonstrate that while wolverine attacks on humans are extremely rare, they do happen under specific circumstances. It’s important to note that these attacks are more often about self-defense than predation.
Are Wolverine Attacks Dangerous?

While wolverines are capable of inflicting serious injuries with their sharp claws and powerful jaws, they are not generally considered a significant threat to humans.
Wolverine attacks typically result in superficial injuries, such as scratches or bites, rather than life-threatening wounds.
Risk of Injury from Wolverine Attacks
- Claws and Teeth: Wolverines have powerful claws and teeth capable of inflicting painful scratches or bites. However, these injuries are usually not deep enough to cause significant harm unless left untreated, potentially leading to infection.
- Aggressive Response: In most cases, a wolverine’s aggressive response is meant to protect itself or its young. A direct attack is unlikely unless the wolverine feels threatened or trapped.
Surviving a Wolverine Encounter
If you do find yourself in a wolverine encounter, it’s important to remain calm and take steps to avoid conflict. Here are some tips for surviving a wolverine encounter:
- Back Away Slowly: Never turn your back on a wolverine. If you see one, back away slowly and give the animal plenty of space to retreat.
- Do Not Run: Running may provoke the wolverine into chasing you, as they can be highly territorial.
- Use Bear Spray: If the wolverine charges or becomes aggressive, use bear spray to deter the animal. Bear spray is an effective deterrent for most wild animals, including wolverines.
Comparisons to Other Dangerous Animals
When compared to other dangerous wild animals, wolverines are less of a direct threat to humans. Larger predators like bears, wolves, or cougars are far more likely to attack humans due to their predatory instincts.
In contrast, wolverines are more likely to avoid humans unless they feel threatened. However, their aggressive defense of territory or offspring can make them dangerous if provoked.
How to Avoid Wolverine Encounters
While wolverine attacks are rare, it’s always best to take precautions to avoid an encounter in the first place. Here are some practical tips for staying safe in wolverine territory:
- Stick to Trails: Always stay on marked trails when hiking or trekking in areas known to be inhabited by wolverines.
- Keep a Safe Distance: If you do spot a wolverine, keep your distance and avoid getting too close. These animals are elusive and will usually avoid human interaction if given space.
- Store Food Properly: Wolverines are opportunistic feeders and may be attracted to food. Use bear-proof containers and store food away from your campsite.
- Avoid Dense Forests: Stay away from areas that may be too dense or rugged for safe travel. Wolverines are more likely to be found in such environments.
Final Verdict: Do Wolverines Attack Humans?
Wolverines are remarkable animals known for their strength, agility, and territorial nature. While they do possess aggressive traits, attacks on humans are extremely rare and typically occur only under specific circumstances, such as when the wolverine feels threatened or is defending its offspring.
Understanding their territorial behavior, survival instincts, and overall behavior will help you appreciate their role in the wild and avoid unnecessary conflicts.
By respecting their space and following safety guidelines, humans can coexist with these fascinating creatures without fear of attack.
FAQs
Could a wolverine kill a human?
It’s very unlikely for a wolverine to kill a human. Wolverines are not naturally predatory towards humans. They are more likely to avoid people unless they feel threatened. Attacks typically happen only if they are cornered or protecting their young.
Are wolverines aggressive?
Wolverines can be aggressive, especially when defending their territory or offspring. They are known for their strong defensive behavior. However, they usually avoid confrontation with humans. They will only act aggressively if they feel threatened.
What do you do if you encounter a wolverine?
If you encounter a wolverine, stay calm and don’t approach it. Slowly back away to give it space. Avoid sudden movements or loud noises that could provoke it. Make sure to report the sighting to wildlife authorities.
Can a wolverine be a pet?
No, wolverines should not be kept as pets. They are wild animals with strong territorial instincts and aggressive behavior. They require a large, natural habitat and can be dangerous. Keeping them as pets is not advisable or legal in many places.
Can a pitbull beat a wolverine?
While pitbulls are strong and tough, a wolverine is incredibly powerful and aggressive. Wolverines have sharp claws and powerful jaws. In a confrontation, the wolverine would likely have the upper hand due to its strength and defensive nature.
What’s the biggest animal a wolverine can kill?
Wolverines can kill smaller animals like rabbits, squirrels, and birds. They are also known to scavenge larger animals, including deer or caribou. Wolverines are opportunistic feeders and can take down weak or injured prey much larger than themselves.
Conclusion: Do Wolverines Attack Humans?
Wolverines rarely attack humans. These animals are known for their solitary nature and usually avoid people. However, if they feel cornered or threatened, they may display aggressive behavior in self-defense.
Attacks typically occur when a wolverine is protecting its young or territory. In general, they are not predatory towards humans and prefer to stay away from populated areas.
To avoid conflicts with wolverines, it’s important to respect their space. Stick to marked trails and avoid venturing into dense wilderness areas where they are more likely to live. If you encounter a wolverine, stay calm, back away slowly, and do not provoke it.
Keeping your food secured and making noise while hiking can also reduce the likelihood of surprising one. By following these simple guidelines, you can greatly reduce the risk of an attack.