Polar bears (Ursus maritimus) are often considered the ultimate predators of the Arctic regions, capable of surviving extreme conditions and hunting seals in one of the harshest environments on Earth. However, as human activities encroach more into their habitat, polar bears attack humans is becoming a growing concern.
So, do polar bears attack humans? What drives these magnificent creatures to harm people? And most importantly, what steps can we take to ensure our safety in polar bear territory?
This survival guide explores these questions in-depth, providing you with the knowledge you need to understand polar bear behavior, the reality of attacks, and the best practices for staying safe when venturing into their realm.
What Are Polar Bears?
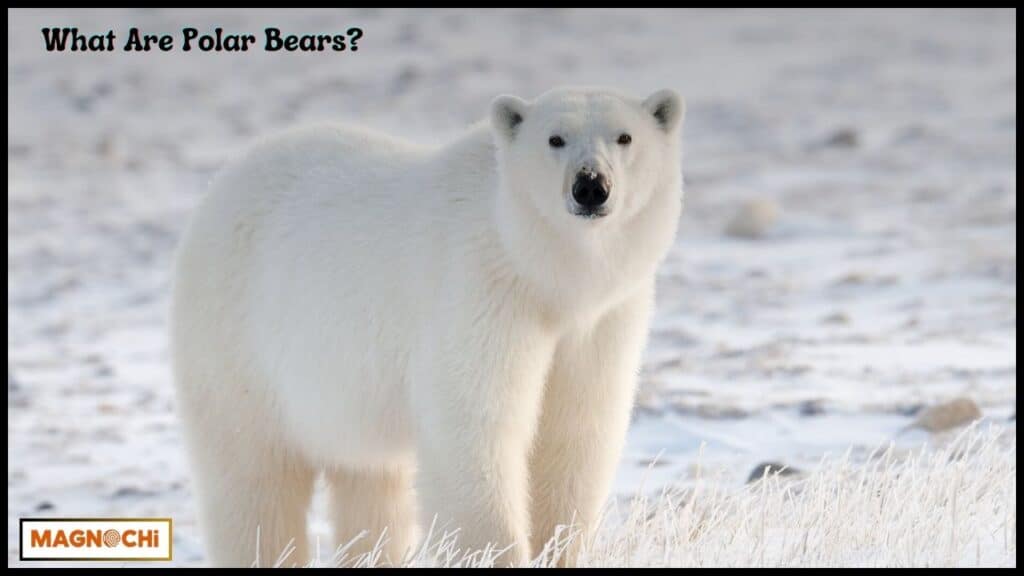

Overview of Polar Bears
Polar bears are large carnivorous mammals native to the Arctic Circle. They are the largest land carnivores and are perfectly adapted to the icy wilderness they call home.
Typically found in regions like Nunavut, Canada, Svalbard, Norway, and Churchill, Manitoba, polar bears are solitary creatures that spend most of their time hunting for seals, their primary food source.
- Physical Characteristics: Adult male polar bears can weigh between 900 to 1,500 pounds, with females generally weighing less. Their fur is white, though technically, it is translucent, which helps them blend seamlessly into their snowy surroundings. Beneath their fur, they have a thick layer of fat to insulate against the freezing temperatures of the Arctic.
- Diet: Polar bears primarily feed on seals, especially ringed and bearded seals, which they catch by waiting near breathing holes in the ice. They rely heavily on the Arctic ecosystem, which includes a combination of sea ice, cold waters, and plentiful seal populations, to sustain themselves.
- Habitat: These majestic creatures are adapted to life in polar regions, using ice floes and the Arctic Ocean as hunting grounds. The climate of the region is brutal, yet polar bears have evolved to thrive in these extreme conditions, relying on thick fur, large paws, and strong swimming abilities.
Polar Bear Behavior
Understanding polar bear behavior is essential to understanding how and why polar bears might attack humans.
As carnivores and apex predators, polar bears have a strict and calculated way of life, shaped by the need to survive in one of the most unforgiving environments on Earth.
- Solitary Nature: Polar bears are solitary animals, except during the mating season and when mothers are with their cubs. Male polar bears are particularly territorial, though they generally avoid conflict with other adults unless it’s over food or mates.
- Stealth and Hunting: One of the defining traits of polar bears is their ability to hunt using stealth. They are patient hunters, often waiting by breathing holes for hours or days to catch a seal when it surfaces for air. Polar bears are incredibly skilled swimmers and can cover long distances in search of prey, and they are equipped with large paws that help them navigate ice floes and snow-covered lands.
- Protective Instincts: Female polar bears, particularly those with cubs, are highly protective of their young. If a mother feels that her cubs are in danger, she will display fierce aggression to defend them, often without provocation.
- Curiosity: Polar bears are naturally curious animals. While they are more likely to approach objects or animals in their environment, their curiosity sometimes leads them to investigate human presence. This behavior can, in some cases, result in dangerous interactions if the bear feels threatened or cornered.
Do Polar Bears Attack Humans?

The Reality of Polar Bear Attacks
Despite their reputation as powerful predators, polar bear attacks on humans are rare. However, when they do happen, the results can be devastating, as polar bears are capable of causing significant harm with their large size and strength.
Understanding the reasons behind these attacks is key to avoiding them.
Reasons for Polar Bear Attacks
Polar bear attacks are often the result of one of the following factors:
- Hunger and Starvation: As climate change reduces the extent of sea ice in the Arctic, polar bears are being forced to travel longer distances in search of food. This disruption in their ability to hunt seals means that some polar bears may become desperate and venture closer to human settlements in search of food. Food scarcity can increase the likelihood of an attack if a bear perceives a human as a potential food source.
- Defensive Aggression: Female polar bears, especially those with cubs, are extremely protective of their young. If they perceive a human as a threat to their cubs, they may attack in self-defense. Aggression is typically not predatory in these situations, but rather a response to perceived danger to their offspring.
- Curiosity: While polar bears do not typically hunt humans, their natural curiosity can lead them to approach humans. A polar bear may be interested in investigating humans or objects in its environment. If the bear feels threatened or is startled, it may escalate the situation into aggression.
- Territorial Behavior: In rare instances, a polar bear may attack if it perceives a human as encroaching on its territory. Male polar bears, particularly during mating season, can exhibit territorial behavior. However, such attacks are exceedingly rare and usually happen in areas where human populations are growing in polar bear territories.
Incidents of Polar Bear Attacks
While attacks on humans by polar bears are infrequent, there have been notable cases that highlight the potential dangers of encountering these creatures.
Some of the most well-known polar bear attack incidents include:
- Nunavut, Canada (2011): In this tragic case, a polar bear attacked and killed a young man in a remote community. The bear had been hungry due to a lack of food in the region, forcing it to venture closer to human settlements. This tragic incident highlights the potential danger of polar bear encounters in increasingly populated Arctic areas.
- Svalbard, Norway (2008): In Svalbard, a group of tourists encountered a polar bear while camping. The bear attacked one of the tourists, resulting in serious injuries. This incident sparked widespread discussions on the safety protocols needed for travelers in polar bear territory.
- Churchill, Manitoba (various incidents): Churchill has seen several polar bear incidents over the years due to its proximity to polar bear habitats. The town has implemented measures such as bear-proof containers, bear alarms, and regular patrols to manage polar bear activity. Despite these efforts, encounters continue to occur, especially during the autumn when polar bears begin to migrate toward the coast.
How Rare Are Polar Bear Attacks?
Polar bear attacks are not common, but they are also not as rare as some might think. They happen most often in regions where human activity intersects with polar bear habitats.
These attacks are more likely to occur in remote, Arctic locations where humans venture into polar bear territories, such as:
- Human settlements: Towns and villages in the Arctic are particularly vulnerable to polar bear attacks when humans encroach on polar bear habitats, either through industry or tourism.
- Increased human-wildlife conflict: The effects of climate change are driving polar bears closer to human settlements in search of food, making encounters more common.
Are Polar Bear Attacks Dangerous?
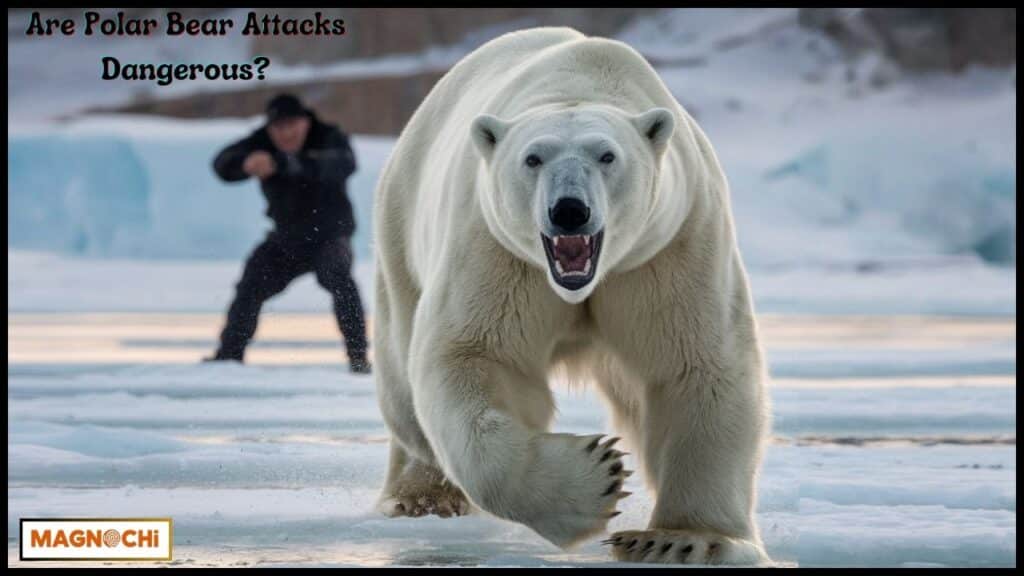

Injuries and Fatalities
When polar bears do attack humans, the consequences can be severe. Polar bears are equipped with powerful jaws and sharp claws capable of inflicting serious harm.
These attacks are more likely to result in fatalities or severe injuries due to the bear’s size, strength, and predatory nature.
- Fatalities: While fatal polar bear attacks are rare, they do occur. The size and power of polar bears make it difficult for humans to defend themselves, especially when the bear is in a predatory or defensive state. In some tragic cases, such as the Nunavut attack, the outcome is fatal.
- Severe Injuries: Polar bear attacks can cause life-threatening injuries, including deep bites and severe lacerations. The bear’s claws are capable of slicing through skin and muscle, and a single strike can be lethal.
Survival Rate and Response to Attacks
Surviving a polar bear attack depends on several factors, including the victim’s ability to defend themselves, their proximity to help, and the severity of the attack.
Self-defense measures, such as bear spray, noise-makers, and other deterrents, can improve the odds of survival, but there are no guarantees.
- Bear Spray: One of the most effective deterrents against polar bear attacks is bear spray. This spray creates an overwhelming scent barrier that can cause the bear to retreat. However, it must be used correctly and only when the bear is within range.
- Other Deterrents: Noise-makers, air horns, and bear alarms can help to alert the bear to human presence and potentially deter an attack. However, these deterrents should be used in combination with bear-proof shelters and campsite security measures to reduce the risk of an encounter.
How to Avoid Polar Bear Attacks?

Precautionary Measures
Prevention is the key to avoiding polar bear attacks. When traveling in polar bear territory, it’s essential to take the necessary precautions to protect yourself and others around you.
- Travel in Groups: Polar bears are more likely to avoid large groups of people. Traveling with others can discourage a bear from approaching, as they typically target individuals rather than groups.
- Food Storage: Bear-proof containers should always be used to store food and waste when camping or living in polar bear territories. Leaving food out in the open attracts bears and increases the risk of an attack.
- Bear-Proof Campsites: Setting up camp in a location with bear-proof fencing or using bear-proof tents can help prevent polar bear encounters. Establishing a safe perimeter and keeping a clean campsite are key steps in minimizing the risk.
- Deterrents: Carry bear spray, a highly effective deterrent against polar bears, as well as noise-makers like air horns, which can help keep a bear at a distance. These tools can help deter a bear before an attack occurs.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Always be aware of your surroundings. Signs that a polar bear may be preparing to attack include growling, huffing, and a direct approach. If you see these signs, back away slowly and use deterrents if
available. - Avoid Attractants: Always clean up food scraps and waste after meals. Human food attracts polar bears, increasing the likelihood of an attack. Bear-proof waste containers and proper disposal methods can help prevent this.
Dealing with an Encounter
If you do encounter a polar bear, remain calm and avoid making sudden movements. Running may trigger the bear’s chase instincts. Instead:
- Stand your ground: If the bear charges, make yourself look larger by standing tall and raising your arms. Do not run or show fear.
- Use Deterrents: If you have bear spray, use it when the bear is within range. The spray can deter the bear from getting closer and can buy you time to escape.
- Stay in Groups: Stick together with others in your group. Polar bears are less likely to approach a large group of people, as the presence of multiple individuals can intimidate them.
Final Verdict
Polar bear attacks on humans are rare, but when they do occur, they can be deadly due to the animal’s immense size, strength, and hunting capabilities. The primary causes of these attacks are hunger, self-defense, and curiosity.
As climate change continues to disrupt the Arctic ecosystem, causing a reduction in sea ice and available prey, polar bears are increasingly venturing into human-populated areas, which could lead to more frequent interactions.
While the risk of an attack remains low, understanding polar bear behavior, recognizing signs of aggression, and taking proper precautions such as carrying bear spray, securing food, and staying in groups can greatly reduce the likelihood of dangerous encounters. Awareness and preparation are key to ensuring safety in polar bear territories.
FAQs
What should you do if you encounter a polar bear?
Stay calm, do not run, and back away slowly. Use bear spray or noise-makers to deter the bear if it gets too close.
Are polar bear attacks more common than other bear species?
No, polar bear attacks are less common than those involving grizzly bears or black bears, though they can be more dangerous due to the bear’s size.
Can polar bears be deterred by bear spray?
Yes, bear spray is an effective deterrent when used properly and can prevent a polar bear from getting closer.
Do polar bears attack humans for food?
Polar bears may attack if they are desperate for food, especially in climate-impacted regions where food sources are scarce.
What are the signs that a polar bear might attack?
Signs of aggression include growling, huffing, direct eye contact, and a bluff charge. Always stay alert and back away if you notice these signs.
Conclusion: Do Polar Bears Attack Humans?
Polar bear attacks on humans are rare, but they do occur, often due to factors such as hunger, curiosity, or defensive behavior.
As climate change disrupts the Arctic ecosystem, polar bears are increasingly coming into contact with humans, leading to more frequent encounters.
By understanding polar bear behavior, taking proper precautions, and using deterrents when necessary, you can significantly reduce the risk of an encounter turning dangerous.
Survival in polar bear territory depends on knowledge, preparedness, and respect for these incredible creatures and their environment.