Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans? Sharks are often associated with danger, especially when it comes to human interactions. But among the various species in the ocean, nurse sharks are one of the most misunderstood.
While many people fear that sharks, in general, may pose a significant threat to humans, the reality of nurse shark behavior is far less intimidating.
Nurse sharks are known for their docile nature and their ability to calmly coexist with humans in their environment. However, questions around whether these sharks attack humans are common, and the nuances of their behavior need to be fully understood to ensure safe interactions.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore nurse shark behavior, examine known shark attacks, and provide you with essential tips for avoiding any risks when encountering nurse sharks.
Whether you’re planning to swim alongside these majestic creatures in the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, or the waters surrounding Central America, this article will equip you with everything you need to know to make your encounter safe and enjoyable.
What Are Nurse Sharks?
Before diving into the specifics of whether nurse sharks attack humans, it’s important to understand what these fascinating creatures are. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Nurse sharks belong to the family Ginglymostomatidae and are among the bottom-dwelling sharks, which means they spend most of their time resting on the ocean floor.
These sharks are often confused with other species due to their size, shape, and behavior.
Physical Characteristics of Nurse Sharks
- Size: Nurse sharks can grow to significant lengths, often ranging from 7 to 10 feet, but some individuals have been recorded to reach 14 feet (approximately 4.3 meters) in length. Despite their size, they are not considered one of the more aggressive shark species.
- Appearance: Nurse sharks have a distinct look. They have broad, flat heads, small, rounded dorsal fins, and their most striking feature is their barbels (whisker-like structures) located around their nose. These barbels are essential for sensing prey on the ocean floor, as nurse sharks are primarily scavengers and bottom feeders.
- Teeth: Nurse sharks have small, flat teeth designed for gripping prey. These teeth are not ideal for cutting through large prey like those of the more aggressive Great White or Tiger Sharks. Their teeth are better suited for crushing shellfish, small fish, and other marine creatures.
- Behavior: Nurse sharks are known for their slow-moving nature. Unlike many other shark species that are known for their speed and agility, nurse sharks tend to glide peacefully along the ocean floor, resting for long periods of time. They are nocturnal feeders, which means they are more active at night.
Habitat and Distribution
Nurse sharks are commonly found in warm, shallow waters, particularly in the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean, and parts of the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
They thrive in areas rich in coral reefs, mangrove swamps, and seagrass beds. These environments provide abundant food sources like crustaceans, small fish, and rays.
Nurse sharks are often seen resting in caves or crevices during the day.
At night, they venture out to forage. While their natural habitat puts them in close proximity to humans, they do not actively seek out human interaction.
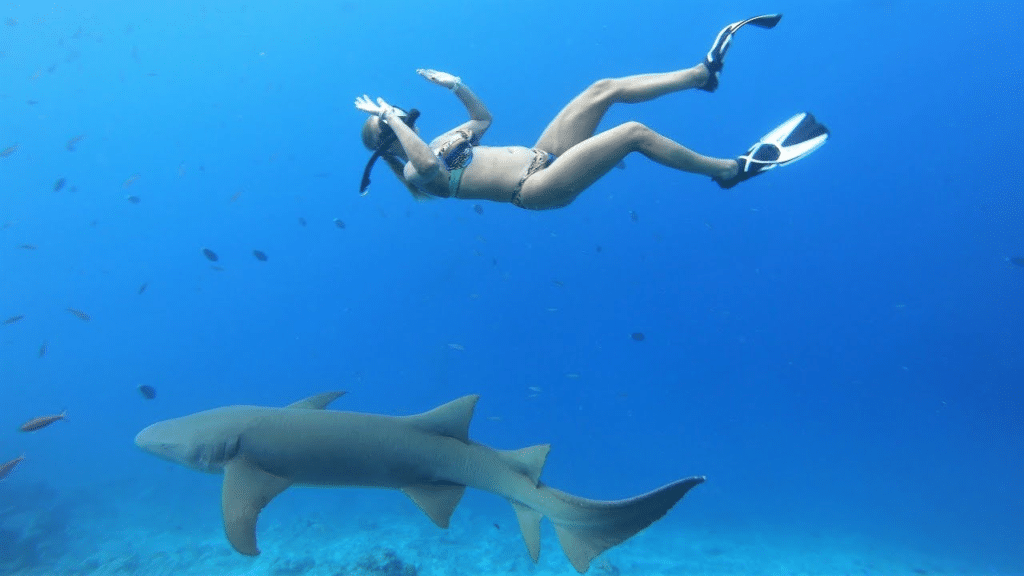

Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?
Given their reputation for being gentle giants of the sea, it’s natural to wonder: do nurse sharks attack humans?
Despite their size and presence in waters often frequented by snorkelers and divers, attacks by nurse sharks on humans are extremely rare.
In fact, nurse sharks are one of the least likely species of sharks to pose a threat to human life. But like any wild animal, there are certain circumstances under which a nurse shark may bite.
To understand these incidents, we need to look deeper into shark behavior and attacks on humans. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Rare Shark Attack Incidents
While nurse shark attacks are uncommon, there have been a few recorded incidents over the years. However, these incidents typically arise from specific circumstances, such as provocation or accidental disturbance. Let’s take a closer look at some of these events:
- Accidental Disturbance: In certain situations, a nurse shark may bite if it feels threatened or startled. This could occur if a diver gets too close to the shark or accidentally enters its personal space, causing it to react defensively. Nurse sharks are generally non-aggressive, but any animal may defend itself if it feels cornered or threatened.
- Provoked Bites: There have been reports where individuals, either out of curiosity or disregard for safety, have attempted to touch or feed nurse sharks. These actions can provoke a defensive response, leading to bites. In many cases, the injuries are minor and occur in non-fatal circumstances.
The Rarity of Nurse Shark Attacks
According to data from the International Shark Attack File (ISAF), nurse sharks account for less than 1% of the total number of recorded shark attacks on humans worldwide.
When compared to other shark species such as Great Whites, Bull Sharks, or Tiger Sharks, nurse sharks are significantly less likely to engage in aggressive interactions with humans.
To put things into perspective, sharks like the Great White and Bull Shark are known for their higher rates of attacks, with far more frequent interactions with humans that result in injuries.
Common Misconceptions
A significant part of the fear surrounding nurse sharks stems from common misconceptions. Many people mistakenly believe that all sharks are inherently dangerous to humans, but this is far from the truth.
While sharks have been misunderstood and demonized in popular culture, most species are not interested in attacking humans. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Nurse sharks, in particular, are known for their peaceful demeanor and are far less inclined to exhibit aggressive behaviors when compared to other species.
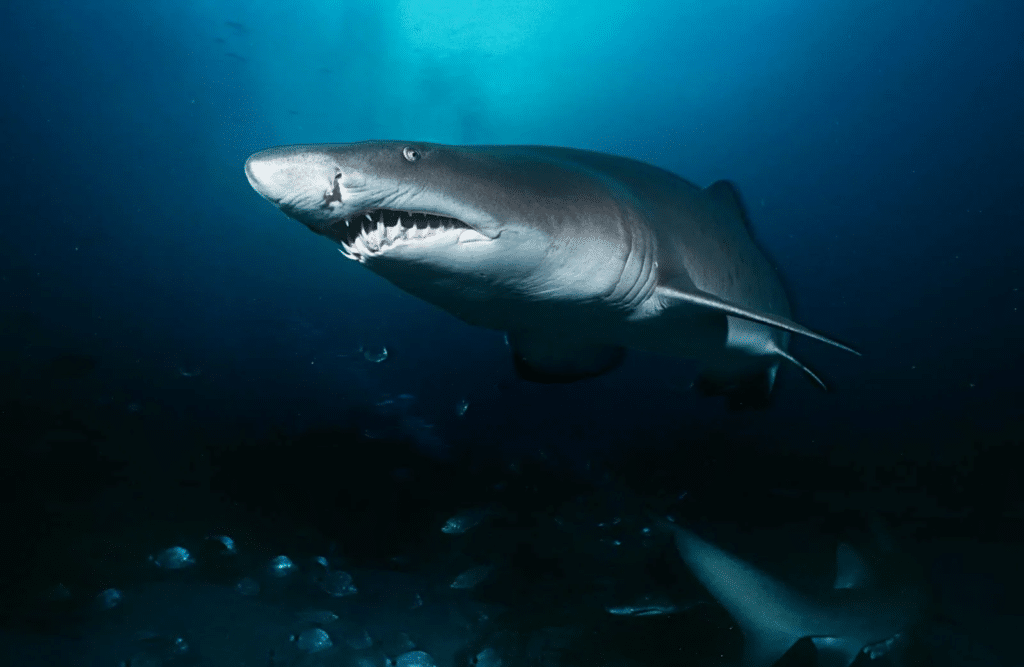

Nurse Shark Behavior: A Closer Look
To understand why nurse sharks rarely pose a threat to humans, it’s important to take a deeper look at their behavior. Unlike some species, nurse sharks are not aggressive hunters.
Instead, they have a unique set of behaviors that make them one of the least likely sharks to interact negatively with humans.
Nocturnal and Lethargic
Nurse sharks are primarily nocturnal, which means they are more active at night. During the day, they often rest in caves or crevices on the ocean floor.
Their slow-moving behavior makes them less likely to chase after prey or become involved in conflicts with humans.
This lethargic behavior is a key characteristic of nurse sharks. While species like the Bull Shark or Hammerhead Shark may chase after fast-moving prey, nurse sharks tend to move slowly, gliding along the ocean floor.
They are generally uninterested in fast-moving animals or humans unless provoked.
Feeding and Scavenging Habits
Nurse sharks are scavengers rather than active predators. They hunt by ambushing smaller creatures, using their barbels to detect prey on the ocean floor.
Their diet typically consists of crustaceans, small fish, and rays. This makes them far less likely to engage in confrontations with larger animals or humans.
Unlike aggressive hunters like the Great White Shark, which actively seek out large prey, nurse sharks are opportunistic feeders.
Their feeding habits help minimize the potential for conflict with humans, as they are more interested in the creatures that share their habitat, rather than actively seeking out interactions with people.
Social Behavior and Interaction with Humans
Nurse sharks are also known to display a calm demeanor when interacting with humans.
Many divers who encounter nurse sharks report peaceful interactions, with the sharks swimming near them without displaying signs of aggression.
They tend to avoid human contact unless provoked, preferring to go about their business in the ocean without seeking out human attention.
Defensive Behavior
Though nurse sharks are not aggressive, they do have the ability to defend themselves if they feel threatened.
If a diver or snorkeler gets too close or makes sudden movements, a nurse shark may react defensively. These bites are usually a form of self-defense rather than an act of aggression.
In most cases, these bites result in only minor injuries, as the nurse shark’s teeth are not sharp enough to cause deep wounds. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Importance of Respecting Wildlife
While nurse sharks are non-aggressive, it’s crucial to treat them with respect in their natural environment.
Marine life is best appreciated from a distance, and any interaction with wild animals should be conducted in a manner that minimizes disturbance.
By following underwater safety guidelines, you can reduce the likelihood of any negative interactions with nurse sharks or other marine life.
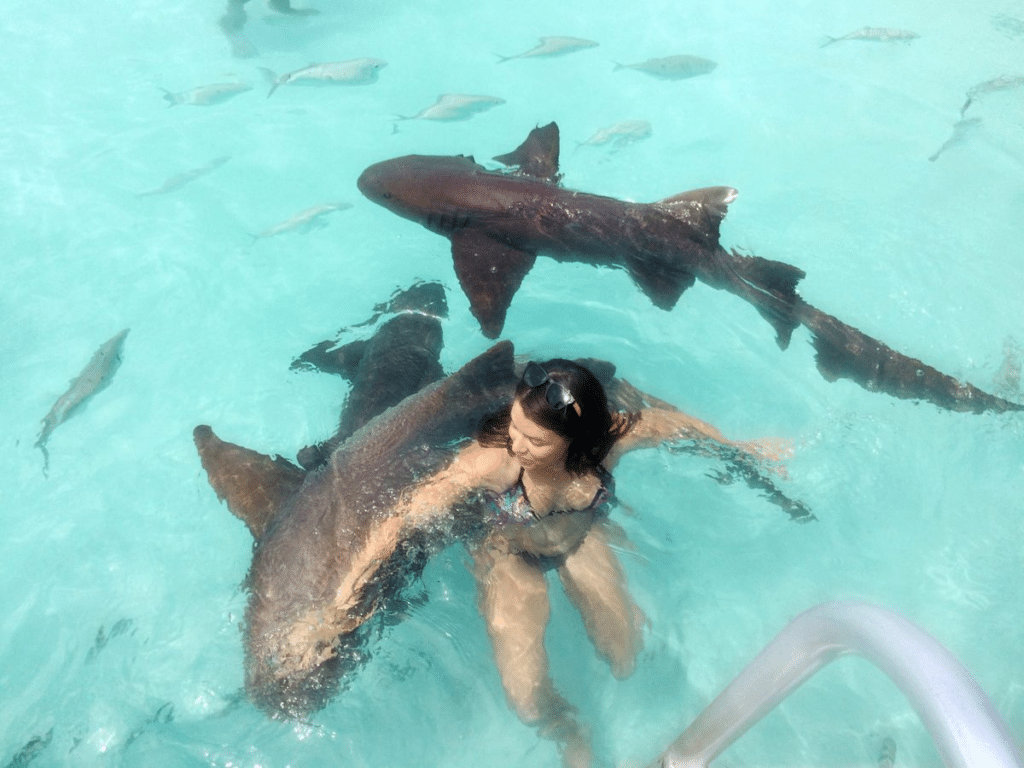

How Dangerous Are Nurse Shark Bites?
While nurse shark bites are rare, it’s important to understand their potential severity. Fortunately, nurse shark bites are generally not as dangerous as those from more aggressive species like the Bull Shark or Great White.
Bite Severity and Injury Risks
- Minor Injuries: Nurse shark bites are often minor, resulting in superficial cuts or bruising. The teeth of a nurse shark are small and flat, designed for gripping prey rather than tearing into large animals. This makes their bites less severe when compared to the injuries inflicted by species with sharper, more specialized teeth.
- Infection Risk: Like any animal bite, a nurse shark bite can lead to infection if not treated properly. It’s crucial to clean the wound immediately and seek medical attention if necessary. If you experience any signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or fever, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Not Life-Threatening: The severity of a nurse shark bite is generally not life-threatening. Most bites can be treated with basic first aid and will heal without complications if properly cared for.
How to Avoid Nurse Shark Attacks
Even though nurse sharks are generally peaceful, it’s important to practice underwater safety to avoid any potential issues. Below are key tips on how to stay safe during encounters with nurse sharks:
Do’s and Don’ts Around Nurse Sharks
Do:
- Stay Calm: Avoid sudden movements. Nurse sharks, like most animals, are more likely to react if they feel threatened or startled.
- Respect Their Space: Always maintain a safe distance from nurse sharks. Never try to touch or interact with them in ways that could disturb their natural behavior.
- Move Slowly: If you need to move around the shark, do so slowly and deliberately. Fast movements may cause the shark to become agitated.
Don’t:
- Don’t Feed the Sharks: Feeding sharks can encourage them to associate humans with food, which may increase the risk of aggressive behavior.
- Don’t Corner the Shark: Always ensure that the shark has plenty of room to escape. If a shark feels trapped, it may bite in self-defense.
By following these simple guidelines, you can safely enjoy your time in the water without worrying about any negative interactions with nurse sharks.
Final Verdict
In summary, nurse sharks do not typically attack humans. While they are capable of biting if provoked or threatened, they are among the most non-aggressive sharks in the ocean.
Most interactions between nurse sharks and humans are peaceful, and the risks of an attack are minimal. These sharks prefer to go about their business of scavenging and hunting small marine animals without seeking out conflict.
If you respect their space, stay calm, and avoid sudden movements, your chances of encountering an attack are slim. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Remember, these sharks are not a danger to humans unless provoked, making them a relatively safe species to observe in the wild.
FAQs
Is it safe to swim with nurse sharks?
Yes, swimming with nurse sharks is generally safe. They are known for their calm nature and usually avoid humans. However, it’s important to respect their space and avoid disturbing them. Following safety guidelines ensures a peaceful encounter.
Do nurse sharks ever bite humans?
Nurse sharks rarely bite humans. When bites occur, they are typically due to accidental disturbances or provocation. Nurse sharks are not aggressive and prefer to avoid confrontation. Always remain calm and respect their space.
What is the number one shark to attack humans?
The Great White Shark is the most known shark species to attack humans. They are responsible for the highest number of recorded attacks. However, most interactions are not predatory, and sharks often mistake humans for prey.
Why don’t grey nurse sharks attack?
Grey nurse sharks are generally not aggressive toward humans. They are shy, nocturnal creatures and prefer to avoid human interaction. They have a reputation for being docile and only bite in self-defense if provoked.
What is the most friendly shark?
The Whale Shark is considered the most friendly shark. They are gentle giants and feed on plankton, making them harmless to humans. Many divers safely swim with them, as they are non-aggressive and calm.
Is snorkeling with nurse sharks safe?
Yes, snorkeling with nurse sharks is safe if done with proper precautions. Nurse sharks are not aggressive, but it’s important to avoid touching or feeding them. Stay calm and keep a respectful distance for a safe experience.
Can you touch a nurse shark?
It’s best not to touch a nurse shark. While they are not aggressive, touching them can cause stress. Respecting their space helps ensure a peaceful encounter and avoids unintentional bites.
What sharks are not safe to swim with?
Sharks like Great Whites, Bull Sharks, and Tiger Sharks are considered more dangerous and should be avoided. These species are known for being more aggressive and have a higher potential to attack humans. Always follow safety guidelines when swimming in shark-prone areas.
Conclusion: Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?
In conclusion, nurse sharks are one of the most peaceful and non-aggressive species of sharks in the ocean. While attacks on humans are rare, they can occur if the shark feels threatened or provoked.
However, these incidents are usually minor and non-fatal. Nurse sharks are scavengers, and their diet primarily consists of small marine creatures, making them far less likely to pose a danger to humans.
When interacting with nurse sharks, it’s essential to practice underwater safety, respect their space, and avoid provoking them.
As long as you maintain a calm and respectful demeanor, your encounter with these gentle sharks will likely be a peaceful and unforgettable experience. [Do Nurse Sharks Attack Humans?]
Read more knowledgeable blogs on Magnochi