Do Wolves Attack Humans? Wolves are one of the most iconic predators, inspiring a wide range of emotions from awe to fear.
The relationship between wolves and humans has been shaped by centuries of myth, legend, and real-world interactions. In popular culture, wolves are often depicted as savage and dangerous, but how accurate is this portrayal?
Do wolves attack humans, and if so, how often does it happen? In this post, we’ll dive into the biology of wolves, the historical and modern-day accounts of wolf attacks, and the real risks posed by these magnificent creatures.
Who Are Wolves?
The Wolf Family
Wolves are part of the Canidae family, which includes other canids like foxes, jackals, and dogs. The gray wolf (Canis lupus) is the most common species found across North America, Eurasia, and parts of Asia.
Wolves are apex predators and play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. As skilled hunters, they primarily target large ungulates, such as deer, elk, moose, and caribou. Wolves work together as a pack, which helps them efficiently hunt and defend their territory.
Physical Characteristics of Wolves
Wolves are powerful animals, with sharp teeth and claws designed for hunting and scavenging.
They can weigh anywhere from 40 to 175 pounds, with the largest wolves being found in northern regions like Canada and Russia. Their large size, muscular builds, and sharp senses of hearing and smell make them formidable predators.
Here are some of the physical characteristics of a wolf:
- Size: Wolves can grow up to 6 feet in length from nose to tail and stand about 2 to 3 feet tall at the shoulder.
- Teeth: Their teeth are sharp and powerful, with incisors that can puncture and shred flesh.
- Senses: Wolves have a keen sense of smell, hearing, and vision, which aids them in hunting and avoiding potential threats.
Wolves are also known for their strong social bonds within their packs. [Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
These packs typically consist of an alpha pair (the breeding pair), their pups, and sometimes extended family members. This social structure is key to their survival.
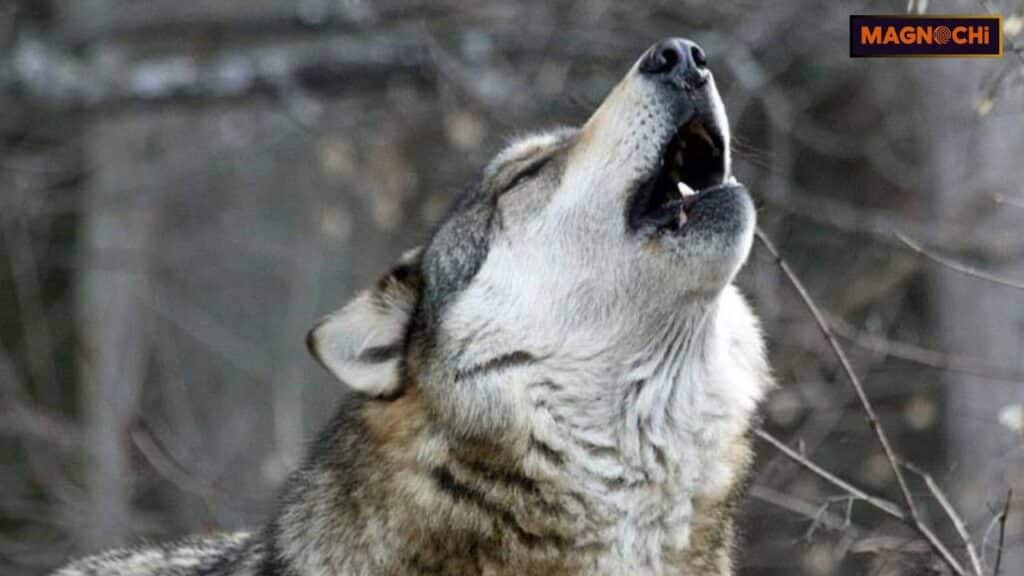

The Biology of Wolves
Wolves have highly specialized biological traits that make them effective predators. Their anatomy and behavior have evolved to ensure survival in harsh environments, hunting large prey, and avoiding predators, including humans.
Wolf Pack Structure
A wolf pack functions like a tight-knit family unit. The pack is usually led by an alpha male and alpha female, who are the breeding pair.
These alphas maintain the pack’s social order, which is crucial for survival. The rest of the pack typically consists of related wolves, such as offspring from previous seasons.
The pack hunts together, typically targeting large prey like moose or elk.
The pack’s success depends on cooperation and a division of labor:
- The alpha pair are responsible for the decision-making and the breeding.
- The beta wolves and subordinates help in the hunting process and contribute to the defense of the pack’s territory.
Wolves as Predators
As apex predators, wolves are skilled hunters. Their predatory behavior is based on the need to provide food for the pack, and their diet mainly consists of ungulates like deer, moose, and elk.
In winter, wolves may also prey on smaller mammals like rabbits, beavers, and rodents, or scavenge from larger animals. [Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
Wolves are highly strategic in their hunting methods, using their keen senses and pack coordination to bring down prey.
Wolves are opportunistic predators, and their hunting efficiency is enhanced by their ability to work as a team. Their success rate in hunting large animals increases dramatically when they hunt in packs.
Wolf Communication Methods
Wolves rely heavily on communication to maintain their pack’s cohesion and to ensure successful hunting. Their methods of communication include:
- Howling: A wolf’s howl is a distinct and powerful sound used to communicate with other pack members, particularly over long distances. It helps wolves maintain territory and coordinate hunts.
- Body Language: Wolves use various body postures, facial expressions, and tail movements to signal their intentions or emotions. For example, the classic “wolf snarl” is a display of dominance or warning.
- Scent-marking: Wolves use scent to mark their territory and communicate with other wolves. They leave scent marks on trees, rocks, and other objects in their territory.
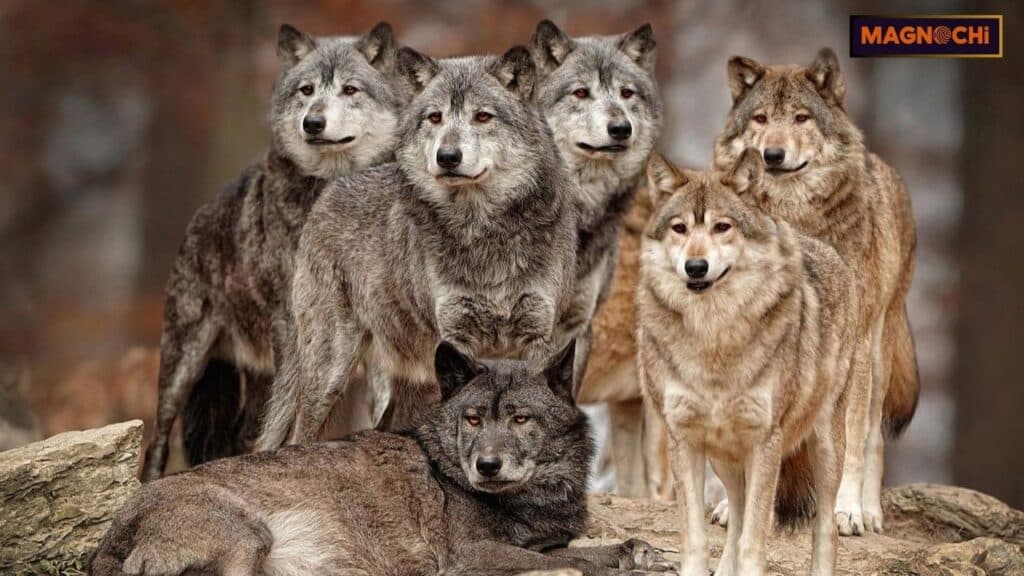

Wolves in Culture and History
Wolves in Folklore
The portrayal of wolves in folklore and popular media is often colored by fear and superstition. In Medieval Europe, wolves were associated with danger, and the rise of wolf hunts in the 16th and 17th centuries is evidence of this deep-rooted fear.
Wolves were often seen as monstrous beasts that posed a threat to humans and livestock.
However, Native American cultures had a more nuanced view of wolves. [Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
The Pawnee tribe and other Native American groups revered wolves as spiritual guides. Wolves were often viewed as symbols of loyalty, strength, and family, and were respected for their role in the natural world.
Wolves in Popular Media
The modern portrayal of wolves in popular media is a blend of romanticized heroism and villainy. Films and books like “The Jungle Book”, “The Grey”, and “Twilight” have contributed to the dichotomy of the good wolf and the bad wolf.
These portrayals often shape the public’s perception of wolves, blending reality with fiction.
Do Wolves Attack Humans? The Real Data
How Often Do Wolves Attack Humans?
While wolf attacks on humans are often sensationalized, they are in fact extremely rare. Wolves typically avoid human contact and are not naturally inclined to attack humans. However, under certain conditions, wolves may become a threat.
- Historical Attacks: Historically, wolves were more likely to come into contact with humans, especially in regions where wolf populations were high and human settlements were encroaching on their territories. In the 18th century, the Beast of Gévaudan terrorized France, reportedly killing dozens of people. However, modern investigations have suggested that the attacks were likely committed by wolves infected with rabies, rather than healthy wolves.
- Modern Attacks: Today, wolf attacks are rarer and typically involve isolated incidents. Studies show that between 2000 and 2010, there were fewer than two dozen recorded wolf attacks on humans globally. These attacks were usually the result of either rabies-infected wolves or wolves that had become habituated to humans through food conditioning.
Do Wolves Attack Humans for No Reason?
Wolves do not typically attack humans without provocation.
Unlike wild cats or other predators that may occasionally target humans, wolves do not view humans as prey. Most attacks occur when the wolf feels threatened or is provoked.
- Rabid Wolves: Wolves infected with rabies are more likely to act aggressively and may attack humans out of fear or confusion.
- Food Conditioning: Wolves that have been fed by humans or are accustomed to human presence are more likely to exhibit bold behaviors, which can lead to attacks, though these incidents are extremely rare.
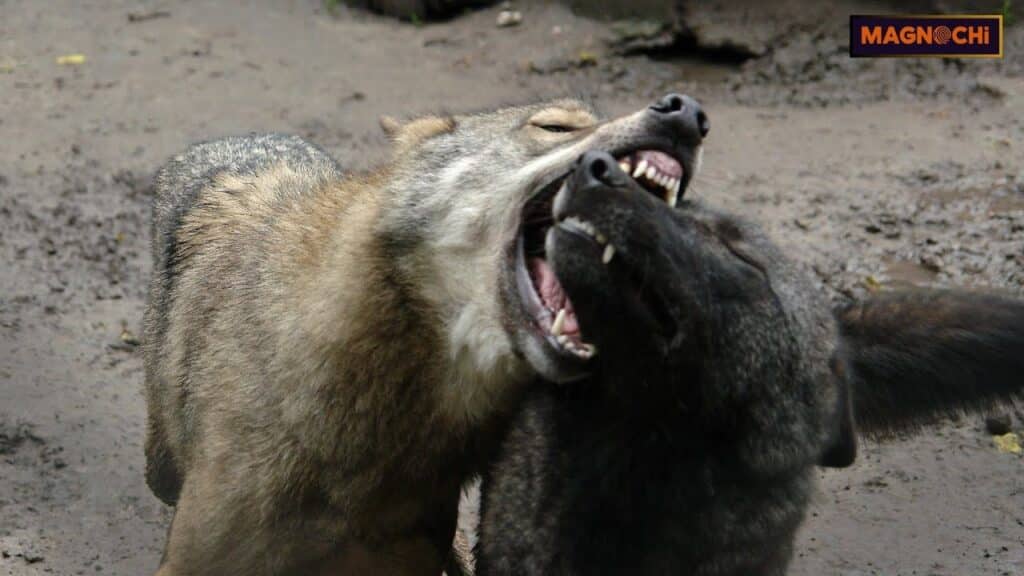

Historical Accounts of Wolf Attacks
The Beast of Gévaudan
One of the most famous incidents of wolf attacks occurred in France during the 18th century. Between 1764 and 1767, a mysterious creature killed between 60 to 100 people in the Gévaudan region. Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
Witnesses described the animal as a large wolf-like creature, and the attacks caused widespread panic. It was later suggested that the animal may have been a rabid wolf or a group of wolves infected with rabies, rather than a single monster.
The Viking Age and Medieval Europe
In Medieval Europe, wolves were often feared and hunted as dangerous pests. Wolves, desperate for food, would sometimes wander into human settlements during the winter months when their usual prey was scarce.
This led to several reports of wolves attacking children, the elderly, and livestock. The fear of wolves during this period contributed to myths and fairy tales, such as the classic story of Little Red Riding Hood.
Modern-Day Incidents
Rare but Real: Modern Wolf Attacks
While wolf attacks on humans are rare, they do happen from time to time. In North America and Eurasia, the reintroduction of wolves into ecosystems has led to more encounters with humans, especially in areas where human settlements border wolf territories.
Wolf populations in the United States have increased in places like Yellowstone National Park, where wolves have been successfully reintroduced.
In these regions, wildlife management practices and safety guidelines have helped reduce the risks of human-wolf conflict.
However, some isolated incidents still occur, often involving wolves that have been exposed to human food or rabies outbreaks.
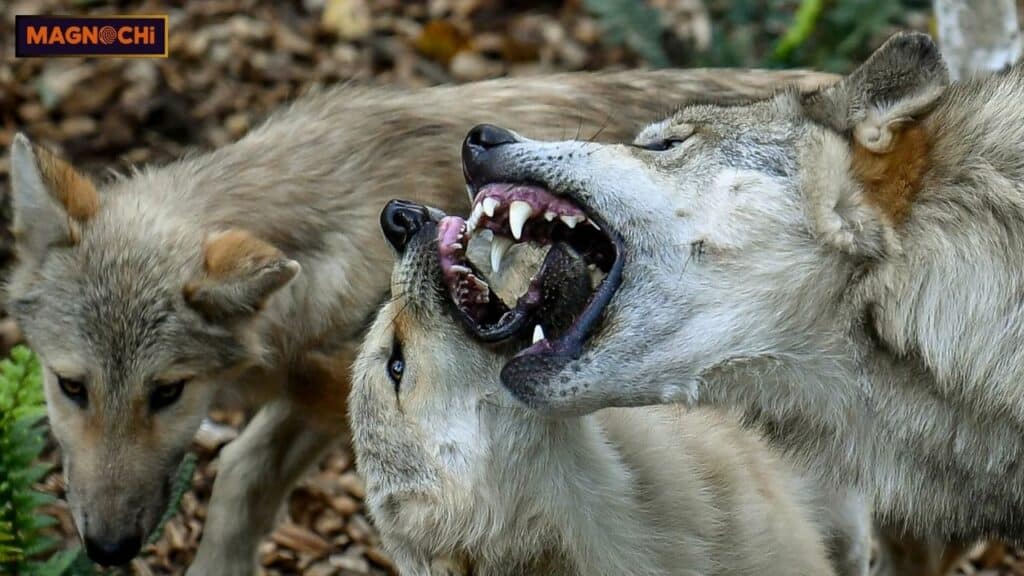

Factors Contributing to Wolf Attacks
Human Behavior and Food Conditioning
Wolves that have been exposed to food sources provided by humans whether through garbage, livestock, or direct feeding can lose their natural fear of humans.
This food conditioning can lead to aggressive behavior and, in extreme cases, attacks on people. This is a significant factor in areas where human-wolf conflict is most likely.
Rabies and Its Role in Attacks
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system, causing wild animals to become aggressive and erratic. [Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
Rabid wolves are much more likely to attack humans, as they lose their fear of people and become overly aggressive. Rabies outbreaks among wolves are rare but can occur in areas where wildlife populations are dense.
Mitigating the Risk of Wolf Attacks
Wildlife Management Practices
Wildlife management plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of wolf attacks on humans. This includes:
- Monitoring wolf populations to track any signs of disease or unusual behavior.
- Habitat protection to prevent wolves from venturing into human settlements.
- Rabies vaccination programs to reduce the risk of infected wolves.
Personal Safety Measures
If you find yourself in wolf territory, taking precautions is key. Some personal safety measures to follow include:
- Never feed wolves or other wildlife.
- Store food securely when camping or hiking in wolf habitats.
- Use bear spray or other deterrents
in case of a wolf encounter. - Stay calm and avoid eye contact or sudden movements if a wolf approaches.
- Keep your pets on a leash to avoid attracting wolves.
FAQs
Are Wolves Dangerous to Humans?
Wolves are generally not dangerous to humans. They are shy, elusive creatures that prefer to avoid human contact. Attacks are extremely rare and usually happen only under certain circumstances, such as when wolves are infected with rabies or have been habituated to human food sources.
How Can I Stay Safe Around Wolves?
If you encounter a wolf in the wild, it’s important to stay calm and back away slowly. Avoid running, as this may trigger the wolf’s instinct to chase. Make yourself appear larger by raising your arms or holding up a backpack.
Can Wolves Be Tamed?
Wolves cannot be domesticated like dogs. While they are social animals, they remain wild and unpredictable. Attempting to tame or keep a wolf as a pet can be dangerous and is not recommended.
Are wolves aggressive to humans?
Wolves are generally not aggressive to humans. They prefer to avoid people and will usually run away if they encounter one. Most attacks occur due to fear, rabies, or food conditioning. They are naturally shy animals.
Will wolves attack you if they see you?
Wolves are unlikely to attack unless they feel threatened or cornered. They are more likely to avoid humans. If you stay calm and give them space, they will typically walk away. Aggressive behavior is rare.
When was the last wolf attack on a human?
Recent wolf attacks on humans are extremely rare. The last recorded fatal wolf attack in North America happened in 2010. Most modern wolf encounters are non-violent. Rabies-infected wolves are a greater concern.
What to do if a wolf approaches you?
If a wolf approaches, stay calm and try to appear larger. Do not run or turn your back. Slowly back away and maintain eye contact. If necessary, use bear spray or loud noises to deter the wolf.
Is wolf friendly to humans?
Wolves are generally not “friendly” to humans, as they are wild animals. They tend to be wary of people and prefer to avoid them. However, in some rare cases, habituated wolves may show bold behavior. Respect and distance are key.
Conclusion: Do Wolves Attack Humans?
In conclusion, while wolf attacks are extremely rare, it is important to understand the circumstances under which they might occur.
Most wolves are not naturally inclined to attack humans.
By respecting wolf habitats, avoiding food conditioning, and taking appropriate precautions when in wolf territories, we can safely coexist with these majestic creatures. [Do Wolves Attack Humans?]
Read more knowledgeable blogs on Magnochi